The increased use of digital technologies is considered as a key enabler for a more sustainable and circular economy. A recent study by the Christian Doppler Laboratory for Sustainable Product Management enabling a Circular Economy at the University of Graz, co-funded by iPoint-systems, provides an overview of how digital technology applications are used for sustainable product management in a circular economy.
By Magdalena Rusch, Josef-Peter Schöggl, Rupert J. Baumgartner
Which digital technologies are included in this study?
The study explores how the internet of things (IoT), big data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and blockchain technology are used in practice and the potential application areas described theoretically. These four technologies were chosen because they are recognized as essential enablers for accelerating the circularity of materials and dematerializing the economy in the European Circular Economy Action Plan (European Commission, 2020).
How can they contribute to a circular economy?
Mobilizing the potential of digital technologies for enhancing the collection, management, and exchange of sustainability-related product data are described as critical enablers for a circular economy (European Commission, 2020). For example, information about the original design specifications of a product can be used to facilitate different R-strategies like reuse, repair, or recycling (Yang et al., 2018).
How are digital technologies helpful for sustainable product management?
146 examples were identified from the literature where digital technologies are applied or could be applied for various sustainable product management activities. 66 examples were identified where an organization was already using digital technologies or where a case study was conducted (these examples are referred to as “applications”). The other 80 examples are only conceptual descriptions of how digital technologies could be used for sustainable product management (referred to as “potentials”).
The assessment revealed the potential of digital technologies in terms of their usability along the product life cycle (divided into the beginning-, middle-, or end-of-life phase), their role as enablers for circular economy strategies (according to the ReSOLVE strategies (EMF, 2015)), and specific sustainable product management areas and outcomes. The latter analysis is shown in Figure 1 below.
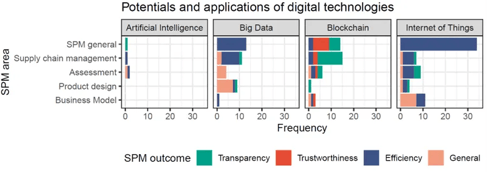
Figure 1: Classification of potential and application examples of digital technologies based on the area of application and the improved SPM outcome (n = 146). Abbreviation: SPM, sustainable product management (Source: Rusch, Schöggl, Baumgartner, 2022).
The 146 examples were described as helpful and classified into the following four areas of sustainable product management: supply chain management, (sustainability) assessment, business modeling, and product design. When an example could not be assigned to one of these four specific areas, the category “SPM general” was used. In addition, the inductive coding of the sustainable product management outcomes resulted in the three categories: efficiency, transparency, and trustworthiness, and also a category for general outcomes was added.
The category of efficiency exhibited the highest frequency (freq. = 82), followed by transparency (freq. = 27) and trustworthiness (freq. = 11). Digital technologies are most frequently described as benefitting sustainable product management in general (overall frequency = 62). Examples of this category are an IoT-based system that enables data-driven recycling decisions using lifecycle information (Kim et al., 2017), the use of IoT sensors to measure the fill levels of scrap metal bins, and suggestions for optimal transport routes inside a factory (Mastos et al., 2020). Most of the examples in this category relate to IoT technology, followed by blockchain technology and big data analytics.
What’s next?
Digital technology applications often entail only incremental improvements, for example, increased efficiency of existing processes, with more radical forms of improvement remaining relatively scarce. Nevertheless, there is clear room for greater adoption and optimization of digital technologies in various areas of sustainable product management to accelerate the transition towards a more sustainable and circular economy.
Where to find the full text?
This study is part of the special issue “Circular disruption: Concepts, enablers, and ways ahead” to advance the conversation on how to best accelerate the transition towards a more circular economy. The full paper “Application of digital technologies for sustainable product management in a circular economy: A review” was published in the Journal “Business Strategy and the Environment” and is available open access here: https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.3099.
References
EMF. (2015). Growth within: a circular economy vision for a competitive Europe. In Ellen MacArthur Foundation, SUN, McKinsey Center for Business and Environment. Retrieved from https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/assets/downloads/publications/EllenMacArthurFoundation_Growth-Within_July15.pdf
European Commission. (2020). A new Circular Economy Action Plan—For a cleaner and more competitive Europe, Pub. L. No. COM (2020) 98 final. European Commission.
Kim, Y. W., Chang, T. W., & Park, J. (2017). Gen2 RFID-based system framework for resource circulation in closed-loop supply chains. Sustainability, 9(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/su9111995.
Kim, Y. woo, Chang, T. W., & Park, J. (2017). Gen2 RFID-based system framework for resource circulation in closed-loop supply chains. Sustainability, 9(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/su9111995
Mastos, T. D., Nizamis, A., Vafeiadis, T., Alexopoulos, N., Ntinas, C.,Gkortzis, D., Papadopoulos, A., Ioannidis, D., & Tzovaras, D. (2020). Industry 4.0 sustainable supply chains: An application of an IoT enabled scrap metal management solution. Journal of Cleaner Production, 269, 122377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122377.
Rusch, M., Schöggl, J.-P., & Baumgartner, R. J. (2022). Application of digital technologies for sustainable product management in a circular economy – a review. Business Strategy and the Environment, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.3099.
Yang, S., Raghavendra, M. R. A., Kaminski, J., & Pepin, H. (2018). Opportunities for Industry 4.0 to support remanufacturing. Applied Sciences, 8(7), 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071177.





