Sustainable product design is more than just a trend; it is a necessity in today’s industrial landscape. As businesses strive to minimize their environmental impact, integrating sustainable product design into manufacturing and engineering processes is crucial. This article explores how product design and sustainability intersect, why it is essential for manufacturers, and how digital solutions support this transition.
The Role of Product Design in Sustainability
Product design directly influences the entire product lifecycle, from raw material sourcing to disposal. By implementing product design for sustainability, companies an reduce waste, optimize energy consumption, and improve product longevity. In a world where resources are finite, businesses must rethink their design strategies to create products that not only meet functional and aesthetic needs but also contribute to global sustainability efforts.
Key Aspects of Sustainable Product Design
Material Selection: Using renewable, recycled, or biodegradable materials to mini-
mize environmental impact and reduce dependence on scarce resources.
- Energy Efficiency: Designing products that consume less energy during production and usage to lower carbon emissions and operating costs.
- Durability and Longevity: Creating products that last longer, reducing resource consumption and minimizing waste.
- Modular and Repairable Design: Allowing for easy repairs and upgrades to extend a product’s lifespan and encourage circular economy principles.
- End-of-Life Considerations: Ensuring recyclability, biodegradability, and responsible disposal to prevent landfill waste and encourage resource recovery.
Differentiating Sustainable Design, Eco-Design, and Circular Design
Eco-design focuses on reducing a product’s environmental impact primarily through the selection of materials, energy-efficient and sustainable manufacturing, and minimizing waste and emissions. It typically addresses environmental aspects during the design phase to lower the product's footprint.
Circular design goes further by embedding principles of the circular economy into the product’s lifecycle. It aims to eliminate waste entirely by designing for durability, reuse, repair, remanufacturing, and recycling, keeping materials and products in continuous use.
Sustainable design, or sustainable product design, takes a broader, more holistic perspective. It integrates both eco-design and circular principles but also considers social and economic impacts. It evaluates the entire lifecycle of a product - from raw material extraction to end-of-life - and optimizes for environmental performance, user well-being, and long-term sustainability.
For deeper insights into circular economy principles, read more on our article on the Circular Economy and Sustainability.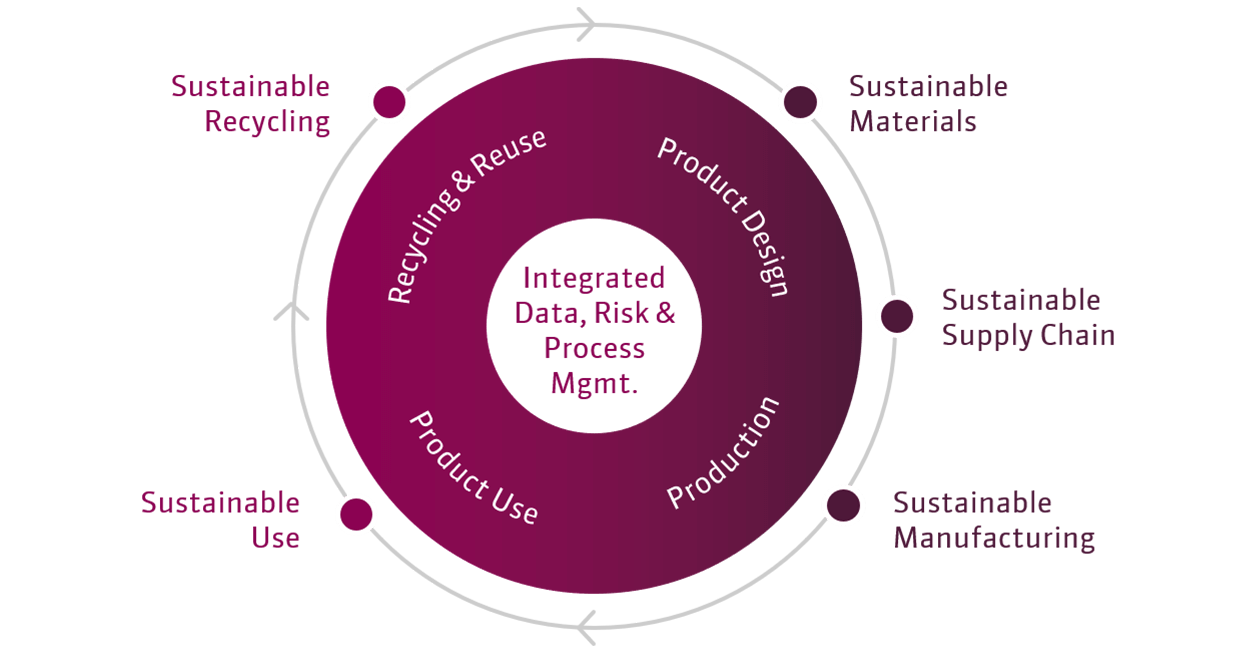
Regulatory Push for Green Product Design
Governments worldwide are tightening regulations to enforce green product design. In the EU, the Ecodesign Directive and Sustainable Products Initiative encourage manufacturers to create environmentally friendly products. Compliance with these regulations helps companies maintain market access, improve brand reputation, and enhance long-term profitability. Companies failing to adopt sustainability measures risk falling behind their competitors as consumer expectations and legal requirements evolve.
Furthermore, sustainability requirements are expanding beyond traditional consumer goods. The EU Green Deal and Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) require companies to disclose environmental impacts, making eco-friendly product design an essential strategy rather than an optional business practice.
Leveraging Technology for Sustainable Product Development
Technology is essential for achieving eco friendly product design. Digital solutions can streamline compliance, track sustainability metrics, and improve product lifecycle management. Companies that adopt these tools can efficiently analyze their environmental impact and adjust production strategies accordingly.
iPoint-systems provides software that supports manufacturers in designing sustainable products:
- Sustainable Design Software: Ensuring compliance with sustainability regulations while optimizing environmental impact.
- Product Sustainability Software: A comprehensive tool for analyzing, monitoring, and improving product sustainability throughout its lifecycle.
- Life Cycle Assessment: A critical method for measuring a product’s footprint to
identify areas for sustainability improvements.
See How Engineers and Product Designers Accelerate Sustainable Design
Book a demo today to discover how product designers and engineers can streamline sustainable design with powerful digital tools.
Industry-Specific Approaches to Sustainable Product Design
Different industries face unique challenges in implementing sustainable product design strategies. While the core principles remain the same, each sector must tailor its approach based on material availability, energy use, and consumer demand.
- Sustainability in the Automotive Industry: Automakers are adopting lightweight materials, electric powertrains, and recyclable components to reduce emissions and energy consumption.
- Sustainability in the Electronics Industry: Electronics manufacturers focus on
modularity, repairability, and sustainable material sourcing to combat e-waste and improve recyclability.
In both the automotive and electronics sectors, leading companies are embedding sustainability directly into product design strategies:
- Jabra reduces environmental impact through recyclable, plastic-free packaging and modular product design, while offering take-back schemes to extend product life and enable responsible recycling.
- Logitech pioneers carbon labeling to promote transparency and guide sustainable consumer choices.
- Fairphone exemplifies modular, repairable design and ethical sourcing to minimize electronic waste and social harm.
- Apple’s Trade-In Program supports circularity by recovering valuable materials for reuse.
- Siemens and Intel focus on energy-efficient semiconductor design and manufacturing, leveraging digital tools to reduce emissions across the lifecycle.

In automotive, companies like Volkswagen, Volvo, and Ford are transitioning to electric mobility, designing for recyclability, and integrating recycled materials into new models. Volvo and Ford also commit to full climate neutrality and responsible sourcing across the value chain. These examples illustrate how sustainable design goes beyond materials, it’s a comprehensive approach to creating responsible, circular, and future-ready products.

Beyond these industries, sectors such as fashion, consumer goods, and industrial equipment are also embracing sustainable product design principles, ensuring long-term resilience and regulatory alignment.
The Business Case for Sustainable Product Design
Beyond regulatory compliance, sustainable product design provides tangible business advantages that contribute to a company’s financial success and market positioning:
- Cost Savings: Optimized use of materials, reduced waste, and lower energy consumption significantly decrease production costs.
- Consumer Demand: A growing number of customers actively seek eco-friendly
alternatives, driving demand for sustainably designed products. - Competitive Edge: Sustainability-driven innovation differentiates brands and allows companies to lead rather than follow market trends.
- Investor Confidence: Businesses demonstrating strong sustainability initiatives attract investors focused on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria.
- Brand Loyalty: Commitment to sustainability fosters stronger customer relationships, leading to higher retention rates and a positive brand image.
Future Trends in Sustainable Product Design
The future of sustainable product design lies in continuous innovation. Emerging trends include:
- AI-Driven Sustainability: Machine learning and AI-powered analytics optimize
material selection and energy efficiency. - Biodegradable and Smart Materials: Innovations in bio-based plastics and self-
healing materials reduce waste and enhance product performance. - 3D Printing for Sustainability: Additive manufacturing reduces excess material use and enables localized production, lowering transportation emissions.
- Digital Twins & Simulation: Virtual prototyping allows companies to refine product sustainability before physical production begins.
As technology advances, sustainable product design will become more accessible and scalable, providing companies with powerful tools to balance profitability and environmental responsibility.
Conclusion
Sustainable product design is no longer optional, it is a critical strategy for businesses aiming to thrive in an evolving regulatory and consumer landscape. Companies that embrace sustainable product design position themselves as industry leaders, ensuring compliance while optimizing efficiency, profitability, and brand perception.
With digital solutions like those offered by iPoint-systems, businesses can integrate sustainability into their core operations and meet future demands seamlessly. 







